In the past few weeks, we learnt about polymorphism, associations and UML class diagram.
The first thing we did is expand our knowledge of inheritance and get to know about a new concept, called polymorphism.
There are four fundamental concepts in OOP: association, polymorphism, inheritance, and encapsulation.
Inheritance is a common form of reusing classes. Programmers could divide classes into hierarchies. The classes in at the top of the hierarchy is called parent or base class, while the ones at the bottom is called child or derived class. Codes can be reused without copying the definitions. A big advantage of inheritance is that programmer can write a section of code in a parent class and use them in many subclass. Inheritance is also one of the associations that indicates the relations between classes, which forms a UML class diagram. This will be talked later. Inheritance means the “is a” relation. For example, student is a person, teacher is a person. If we see them as classes, them all of them are person, but students and teachers have some additional parts other than basic person, while the common part can be reused to reduce the time of developing.
Polymorphism is another element in OOP. It means the subclasses of a super class have their own unique behaviors but share some basic functions. It can treat the child classes as they are the super class. There are two actions in polymorphism: overriding and overloading. Different parameters mean overloading, while exactly same name and parameter mean overriding.
After learning these relations, we tried to add these relations into the UML. The relations between classes in the UML is called associations. In association, we use multiplicity to indicate how many classes does an association could refer to. There are three relations in association: aggregation, inheritance and dependency.
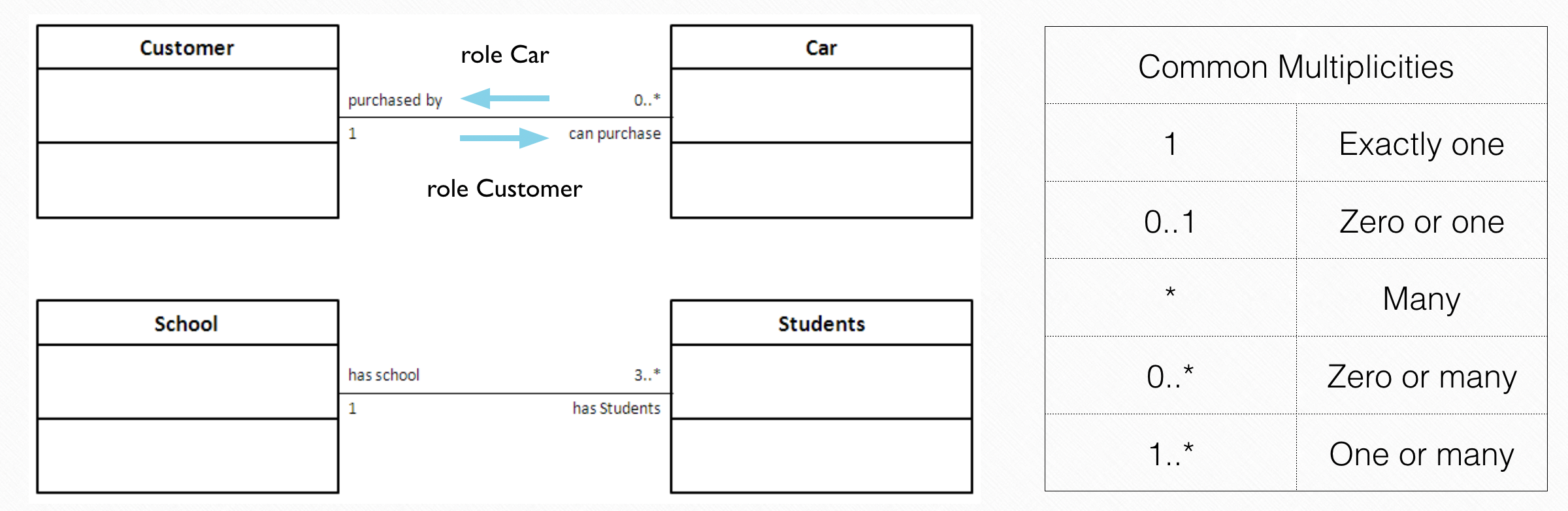
Aggregation is also known as “has a” relation, represented by a hollow diamond. For example, a department could have several teachers inside, then “teacher” class and “department” class forms an aggregation.
Inheritance is also known as “is a” relation, represented by a hollow triangle.
Dependency is also known as “rely on” relation, represented by a normal arrow. For example, the main class want to use “FileIO” class, then it can directly use it without write again.
During the week, we had two reading homework. The first one is telling us the concept of decomposition in OOP. The concept “object” helps people to reduce a large problem into a simple symbol to deal with, so that the problem is easier to solve. The second reading tells us that it is not true that the more dependencies, the better the solution is. Sometimes too much dependencies would increase the complexity of the program and cause problems of managing the project. Programmers need to learn to reuse existing code to lower the complexity and readability of the programs.
Homework
The homework is to draw a class diagram that represents the associations in our IA project.
