These weeks, we learnt about application softwares and operating system (OS).
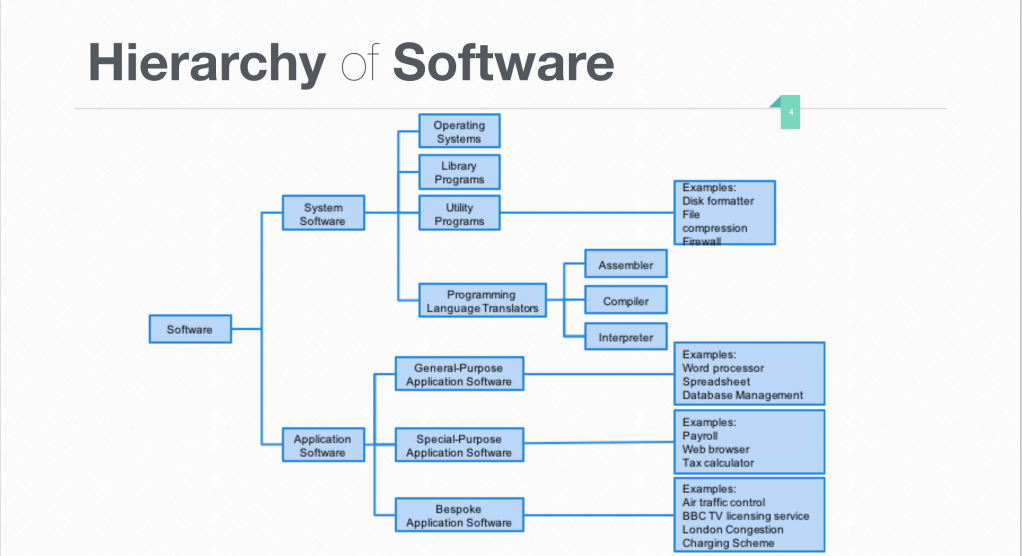
In general, software can be divided into two categories: system software and application software. System softwares are those who can communicate with the system, or the program. For example, translators (including compiler, all at once; interpreter, line by line; assembler, assembly language to machine language) are one kind of system software.
Application Software
Unlike system software, users can directly communicate with application software. They allow users to perform non-computer tasks. They can be divided into three categories: general purpose, special purpose and bespoke.
Word processor refers to the application softwares that allow users to create documents. It includes tools and functions for the composition, editing, formatting and printing of documents. Microsoft Word and Pages are both word processors.
Spreadsheets allow users to organize and analyze data. In spreadsheet data is presented in cells, the basic unit to input a single unit of data. Users can create charts or graphs to visualize the data. However, it can only hold limited amount of data. Excel and Numbers are both spreadsheet softwares.
Database Management System (DBMS) provides interface between users and database. Database is an organized collection of data that includes records (rows) and fields (columns). Key in DMBS is one or more specific columns that uniquely identify each row. DBMS helps users to creates, stores, updates, modifies and extract information from database. Microsoft Access, MySQL, Oracle are all DBMS.
Email allow users to exchange digital message (in the form of a letter) from single user to one or multiple recipients. The client is used to manage those emails. The author and recipients do not have to be online at the same time to exchange the message. Outlook and Gmail are both email clients.
Browser allows users to access, retrieve, and present content (web pages, images, videos or other files identified by a URI, which is Uniform Resource Identifier) from the World Wide Web (WWW). It request the wanted information and display it for the users. Safari and Edge are both browsers.
Computer-aided Design (CAD) allows users to create, modify, analyze and optimize a digital design. It helps the designers to do faster and better. Designers can view the prototypes in the software and show it to clients before actually producing them. Auto CAD and Cinema 4D are both CAD softwares.
Graphic processing software allows users to manipulate or edit images on a computer. Photoshop is an example of graphic processing software.
Mail Merge
Mail merge is a function in word processor, spreadsheet and email clients that allows users to personalize their information in a general model. It’s a type of batch processing, because users only need to prepare one model and names, then they can produce all the needed personalized information in a second.
Features of Application Software
Application have some common features.
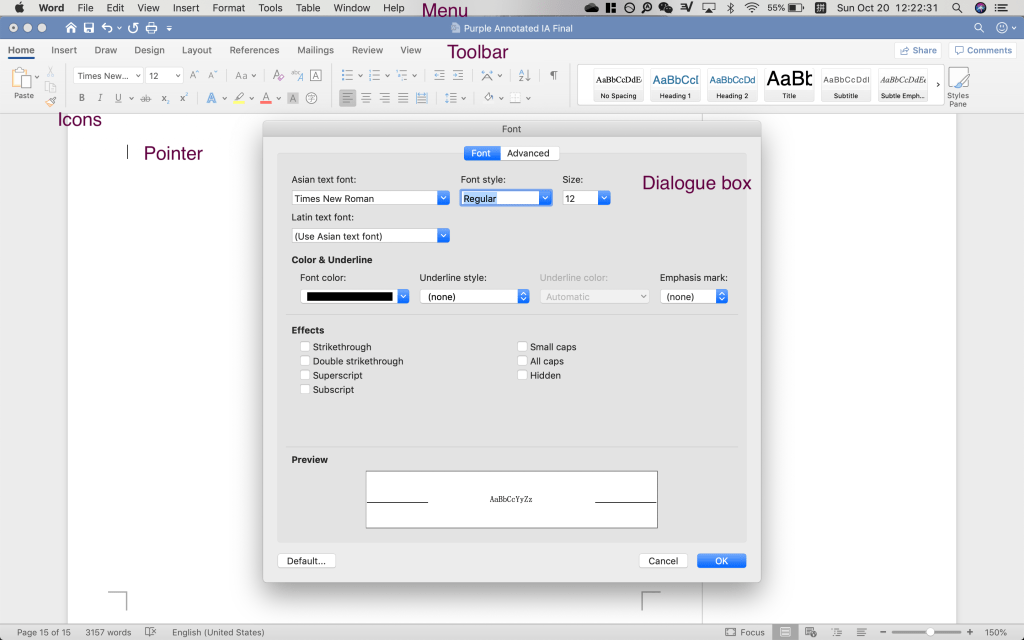
Toolbar provides functions related to the purpose of the software.
Menu categorizes commands with similar functions into groups.
Dialogue box asks users to do certain commands (verification, for example).
Icons give users the first impression of a function and make the instruction of functions easier to read.
GUI Components: including Pointers (including mouse pointers and the input indicator) tell users where they are currently at.
These features are usually extracted from the library provided by the operating system. Different OSs, like macOS and Windows, have different features. GUI, for example, use the library. It increase the usability of softwares.
Functions of OS
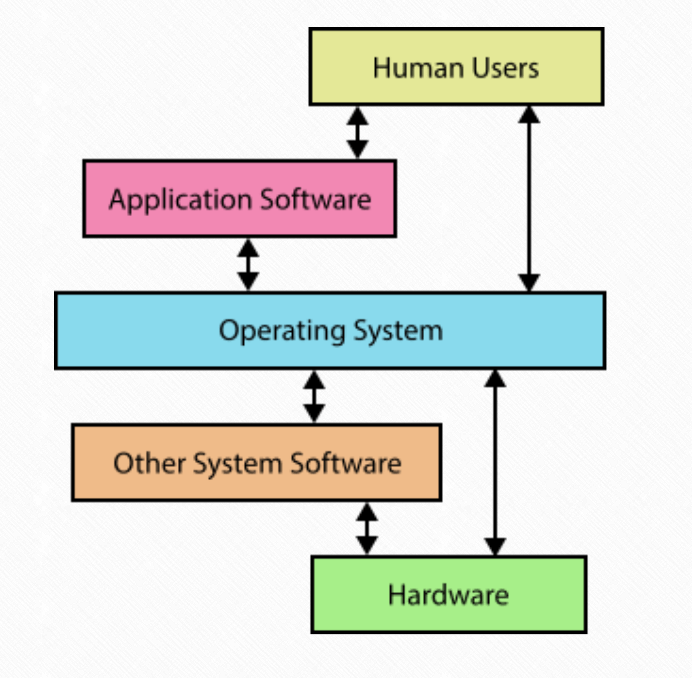
OS is a set of softwares that control the computer’s hardwares and provides services for computer programs. It acts as a middle-man between software application and computer hardwares. It also provides a platform for users to use applications.
Provides a user interface:
As people are more comfortable with graphic or textural information but not binary data, OS provide user interface to hide the complexity behind those graphics.
- CLI: command line interface
- GUI: graphic user interface
- NLI: natural language interface
- MBI: menu based interface, give users a selection of options
Memory management: OS manages how memory should be used by applications. It make sure that a unit of memory is only used by one application at a time. If more application try to use the memory, the latter may cause data loss (overwritten). When a memory location is full, the OS send a confirmation message to other applications so that they do not cause data loss.
Resource monitoring and multi-tasking: tasks in a queue is given time slices; after each run a time slice, they have to wait at the end of the queue again. Because the switch is short, it looks like the computer is doing multi-tasking. Every day, when we open multiple programs, our computers are all doing multitasking.
Peripheral management: OS use device manager to control the input and output peripherals. It’s like a bridge between OS and the peripherals. For example, some “printing wizard” in our computer is a peripheral management software.
Disk access and data management: OS use file manager to organize (move, copy, delete) the files and folders. OS ensure better use of space and provide reliability and fast access time. It prevent data loss (overwriting of other application) and coordinate the data exchange between primary memory and disk file.
Security management: OS prevent unauthorized access to files and give privileges to certain accounts or programs. For example, some application need the right to access to the internet, and some need the right to read and write files from the disk.
Networking management: OS allows the sharing of resources, like storage. It acts as a middle man between applications and networks.
OS Resources Management Techniques
Scheduling:
Policies:
Virtual memory: when the primary memory is not enough, OS will use part of the hard disk as virtual memory to increase the capability of processing.
Paging:
Interrupt: a signal to the processor sent by hardware or software indicating a need of immediate attention. To reply this request, the OS suspends its current activities, saving its state, and calls interrupt handler to deal with the situation.
Polling: a period check of devices to see what state they are and whether they are connected or wanting to exchange data. Polling will identify the fact that a device is ready to exchange data.